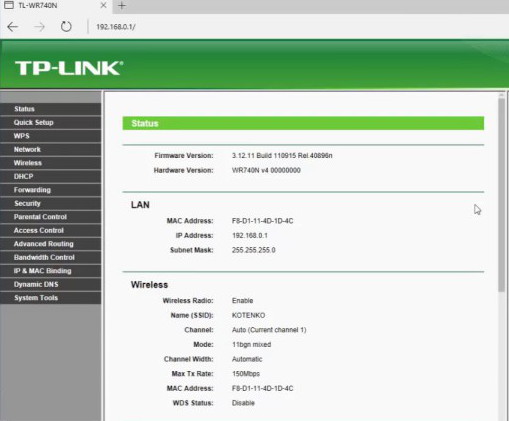
The IP address, 192.168.0.1, is commonly reserved as the default IP for many broadband network routers used within homes. It is a private IPv4 network address implemented within home or corporate computer networks. It is preconfigured by the network router manufacturer which helps in accessing the router’s administrative console. It lies within the IP address range of 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255 and is defined in RFC 1918: Address Allocation for Private Internets.
192.168.0.1 IP address is frequently used to while setting up a network LAN (Local Area Network) using any network router. Router’s administrative console can generally be accessed by accessing http://192.168.0.1 in a web browser. The following interface which opens on authentication (using username and password) acts as the single point of control for administering and managing the router configuration. The default credentials to access the administrative console is commonly given in the router’s manual or manufacturer’s official website. As a standard rule, the IP 192.168.0.1 cannot be used by multiple network devices on the same network, or else it may lead to IP clash or network downtime.
In spite of being the default IP for a router, it can definitely be modified to any other suitable IP. Though, generally not required , the change in IP is needed rarely by administrators to resolve clashes.
Troubleshoot 192.168.0.1
Like anything else in the world, 192.168.0.1 is likely to fail or face issues. Given below are the most common problems those occur with 192.168.0.1 IP.
#1: Default credential
Most network routers come with a predefined username and password. The most common username/password combinations are admin/admin and admin/password. It is highly recommended that you login to your administrative console and change the password immediately in order to avoid any security violation. The router manual or manufacturer’s website is the best place to start looking for the default credentials.
#2: Firewall blocking
If the administrative console page doesn’t open or load, some firewall policy could be blocking the access. Do check your firewall settings and exclude 192.168.0.1 from all restrictions.
#3: Wrong IP
Different manufacturers configure their router with different IP addresses. It’s recommend to crosscheck the default IP address for your router in the product manual or manufacturer’s website.
#4: Faulty network mask
The administrative console page may not open or load due to faulty setup of network mask. A test on the network mask configured for computers on the same network is necessary; they should be same (setting the mask to 255.255.0.0 could be a viable resolution).
#5: Wireless access
The administrative console page may not load sometime if it is being accessed wirelessly, i.e. using wi-fi connection. It’s recommended that you connect the router directly to the computer using a LAN cable.
#6: Finding IP
While connected to your router via LAN, you can run ipconfig /all or tracert 4.2.2.1 in the command prompt to get the router’s default IP. On running Tracert command, the first IP that pops up could be your router’s IP.
#7: Factory restoration
Not always, but resetting your router to the default Factory settings and reconfiguring can help solve any faced issue.
The above tips should help you resolve any issue faced with 192.168.0.1. If you find any other issue not listed here, please feel free to discuss it in the below comments.